ArrayList深入分析
基本方法
使用由 toString() 方法提供的默认的转换显示类集的内容,toString() 方法是从 AbstractCollection() 继承下来的。对于例子来说足够,但是通常情况下会重写此方法。
1 | public class ArrayListTest1 { |
结果
1 | hello |
包装类与原生数据类型测试
1 | public class ArrayListTest2 { |
结果
1 | hello |
包装类型的遍历与操作
1 | public class ArrayListTest3 { |
结果
1 | 18 |
从数组列表(ArrayList)获得数组(Array)
当使用 ArrayList 时,有事想要获得一个实际的数组,这个数组包含了列表的内容。可以通过调用
toArray() 来实现它。下面是几个为什么可能想讲类集转换成为数组的原因:
- 对于特定的操作,可以获得更快的处理时间
- 为了给方法传递数组,而方法不必重载去接收类集
- 为了将新的基于类集的程序与不认识类集的老程序集成
Arrays.asList()返回一个受指定数组支持的固定大小的列表。(对返回列表的更改会 “直写” 到数组)。此方法同
Collection.toArray() 一起,充当了基于数组的 API 与基于 Collection 额 API 之间的桥梁
1 | public class ArrayListTest4 { |
结果
1 | 1 |
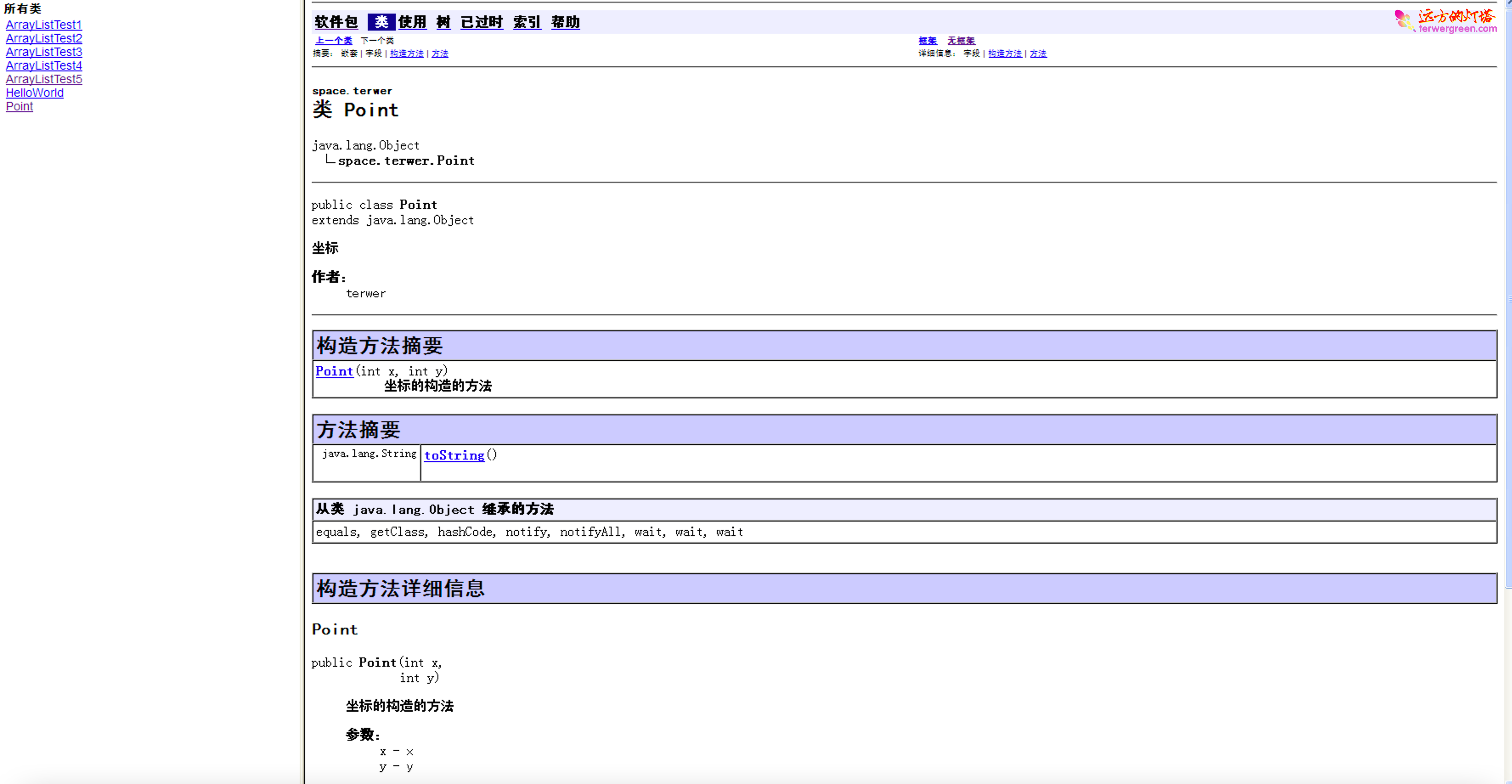
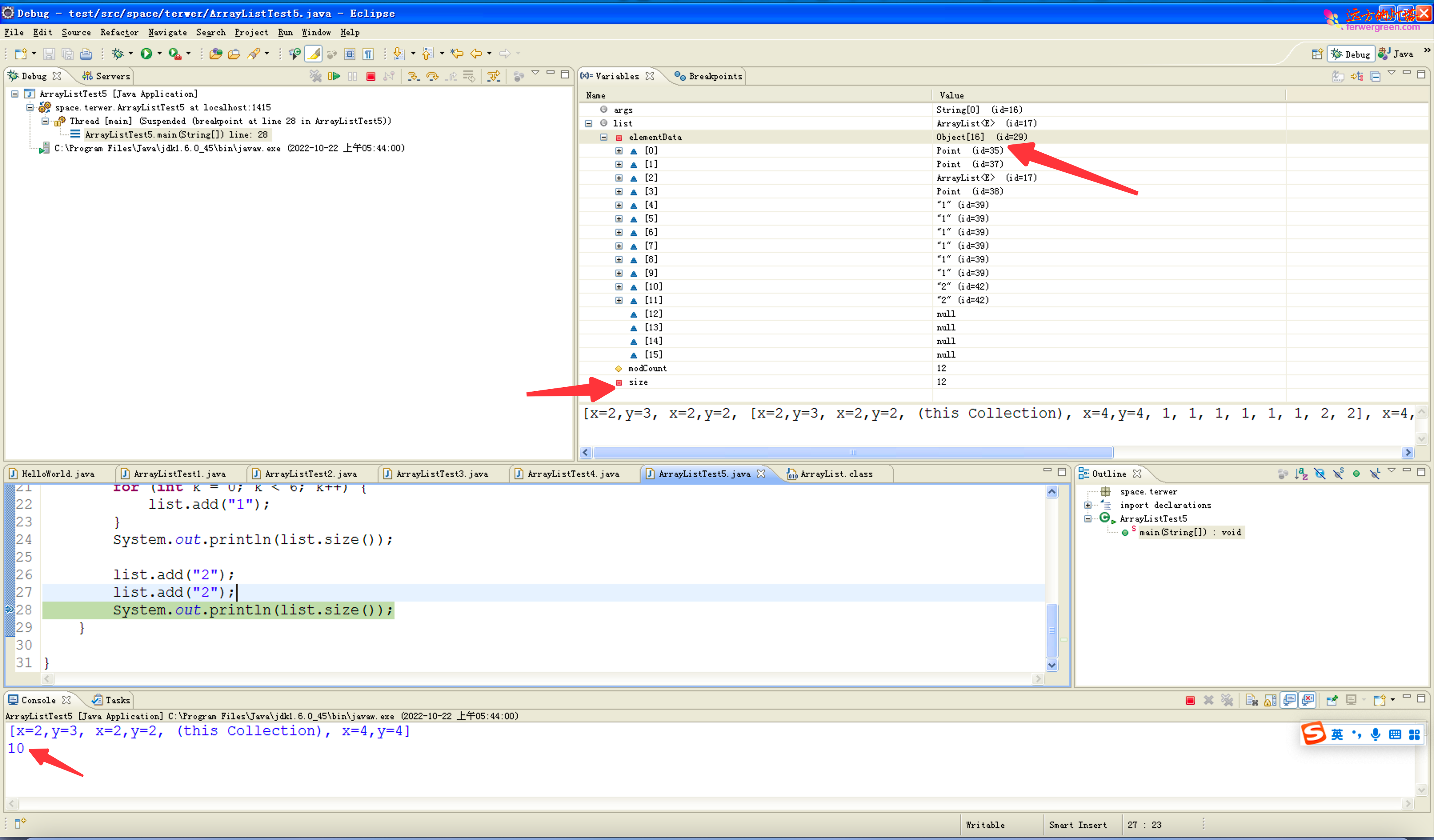
ArrayList 操作自定义对象
1 | public class ArrayListTest5 { |
结果
1 | [x=2,y=3, x=2,y=2, (this Collection), x=4,y=4] |
需要注意的几点
集合中存放的依然是对象的引用而不是对象本身。
ArrayList 底层使用数组实现,在 JDK1.6,当使用不带参数的构造方法生成 ArrayList 对象时,实际上会在底层生成一个长度为 10 的 Object 类型数组。
1
2
3
4
5
6/**
* Constructs an empty list with an initial capacity of ten.
*/
public ArrayList() {
this(10);
}注意:从 Java7 开始,已经不是在构造方法初始化为 10,而是在 add 方法检测,然后调用 grow 方法初始化为 10。Java7-Java17 都改变了这个策略。
Java17 沿用了这一策略。不是在初始化里面初始化的 10,而是在 add 的时候检测到不够才初始化的 10。Java17 源码分析如下:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35private static final int DEFAULT_CAPACITY = 10;
private static final Object[] DEFAULTCAPACITY_EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA = {};
public ArrayList() {
this.elementData = DEFAULTCAPACITY_EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA;
}
public boolean add(E e) {
modCount++;
add(e, elementData, size);
return true;
}
private void add(E e, Object[] elementData, int s) {
if (s == elementData.length)
elementData = grow();
elementData[s] = e;
size = s + 1;
}
private Object[] grow() {
return grow(size + 1);
}
private Object[] grow(int minCapacity) {
int oldCapacity = elementData.length;
if (oldCapacity > 0 || elementData != DEFAULTCAPACITY_EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA) {
int newCapacity = ArraysSupport.newLength(oldCapacity,
minCapacity - oldCapacity, /* minimum growth */
oldCapacity >> 1 /* preferred growth */);
return elementData = Arrays.copyOf(elementData, newCapacity);
} else {
return elementData = new Object[Math.max(DEFAULT_CAPACITY, minCapacity)];
}
}
add 方法剖析
**在 JDK1.6 中,如果增加的元素个数超过了 10 个,那么 ArrayList 底层会生成一个数组,长度为原来数组的 **1.5倍+1 ,然后将原数组的内容复制到新数据当中,并且后续增加的内容会方法哦新数组当中。JDK7 以后该规则有所变化,长度是原来数组的 1.5倍 。当新数组无法容纳增加的元素时,重复该过程。1
2
3
4
5public boolean add(E e) {
ensureCapacity(size + 1); // Increments modCount!!
elementData[size++] = e;
return true;
}不够扩展 1.5 倍
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12public void ensureCapacity(int minCapacity) {
modCount++;
int oldCapacity = elementData.length;
if (minCapacity > oldCapacity) {
Object oldData[] = elementData;
int newCapacity = (oldCapacity * 3)/2 + 1;
if (newCapacity < minCapacity)
newCapacity = minCapacity;
// minCapacity is usually close to size, so this is a win:
elementData = Arrays.copyOf(elementData, newCapacity);
}
}
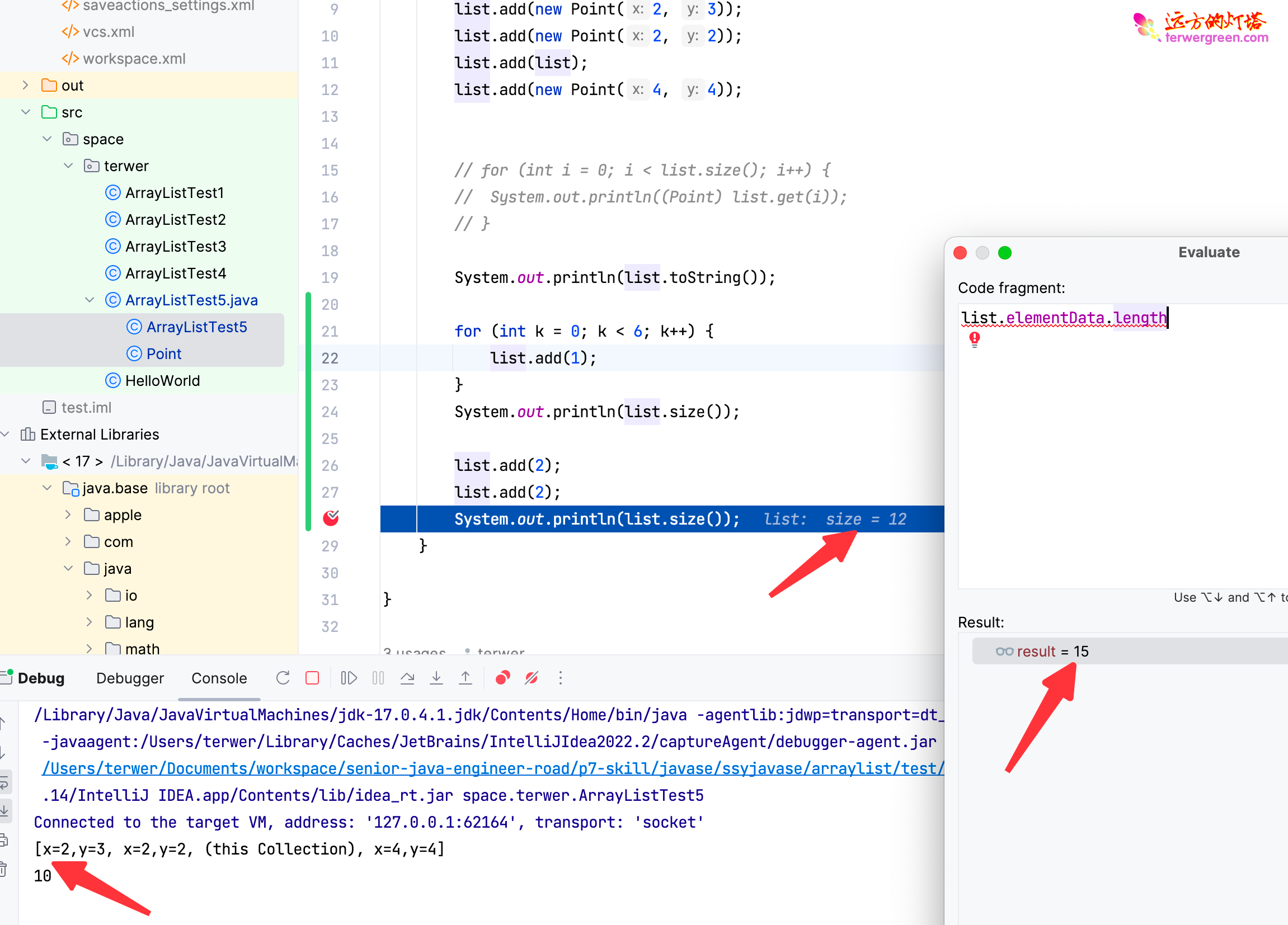
注意:Java7 以后增长的方式更加优雅,是用 位运算 计算的,效率更高。
https://stackoverflow.com/a/52355461/4037224
例如,Java17 的实现如下:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11private Object[] grow(int minCapacity) {
int oldCapacity = elementData.length;
if (oldCapacity > 0 || elementData != DEFAULTCAPACITY_EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA) {
int newCapacity = ArraysSupport.newLength(oldCapacity,
minCapacity - oldCapacity, /* minimum growth */
oldCapacity >> 1 /* preferred growth */);
return elementData = Arrays.copyOf(elementData, newCapacity);
} else {
return elementData = new Object[Math.max(DEFAULT_CAPACITY, minCapacity)];
}
}
对于 ArrayList 元素的删除操作,需要将被删除元素的后续元素向前移动,代价较高。
集合当中只能防止对象的引用,无法放置原生数据类型,在 JDK1.5 以前,我们需要使用原生数据类型的包装类才能加入到集合当中。
集合当中放置的都是 Object 类型, 因此取出来的也是 Object 类型,因此必须要使用强制类型转换将其转换为真正的类型(放置进去的类型)。
生成 javadoc
eclipse 点击 project->Generate javadoc
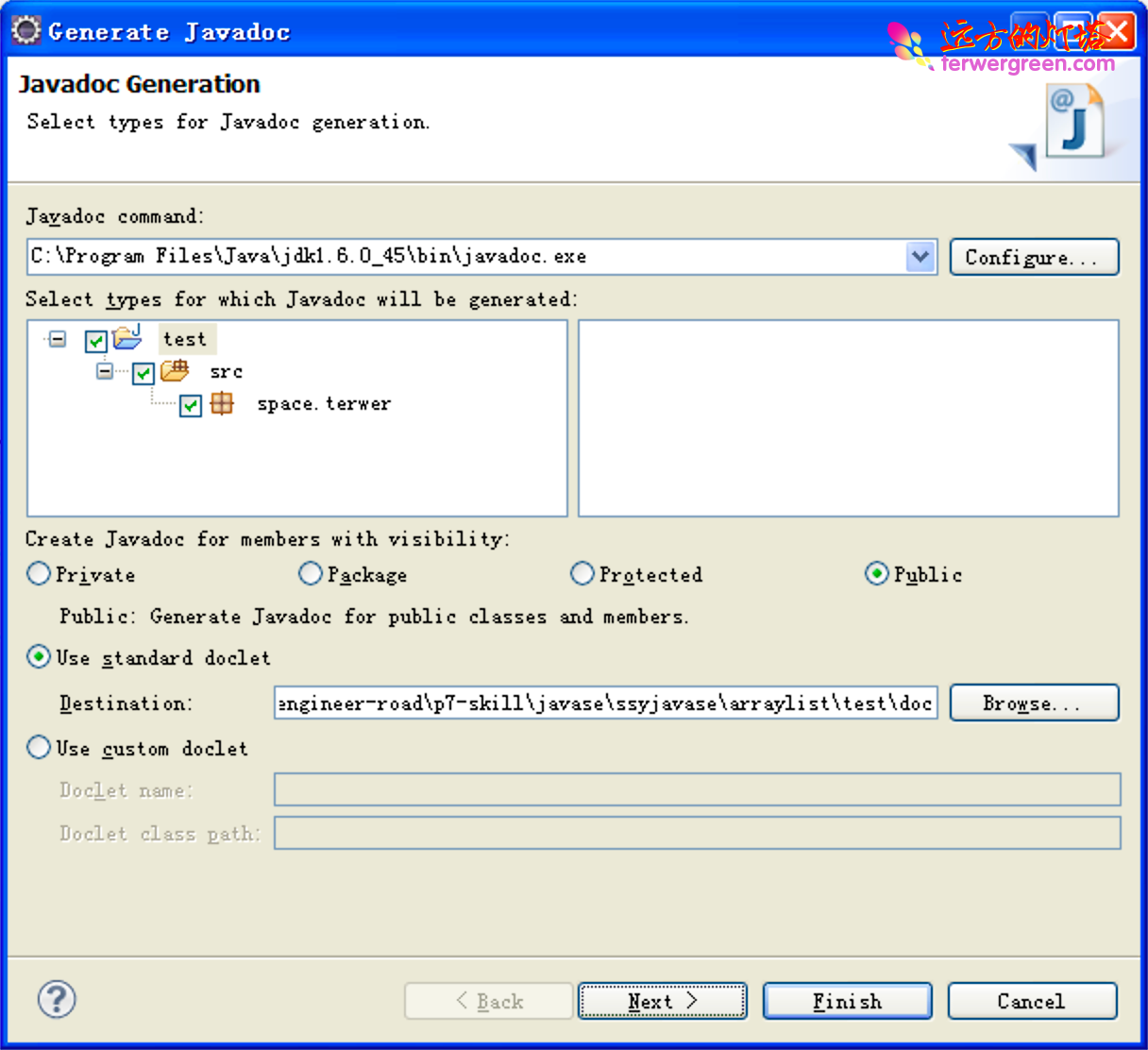
解决Eclipse生成的注释文档中文乱码问题
给 javadoc.exe 加上编码参数就 OK。
具体的:
**在 Eclipse 里 export 选 JavaDoc,在向导的最后一页的 **Extra JavaDoc Options 里填上参数即可。
比如项目采用的是 UTF-8 的编码就填:-encoding UTF-8 -charset UTF-8
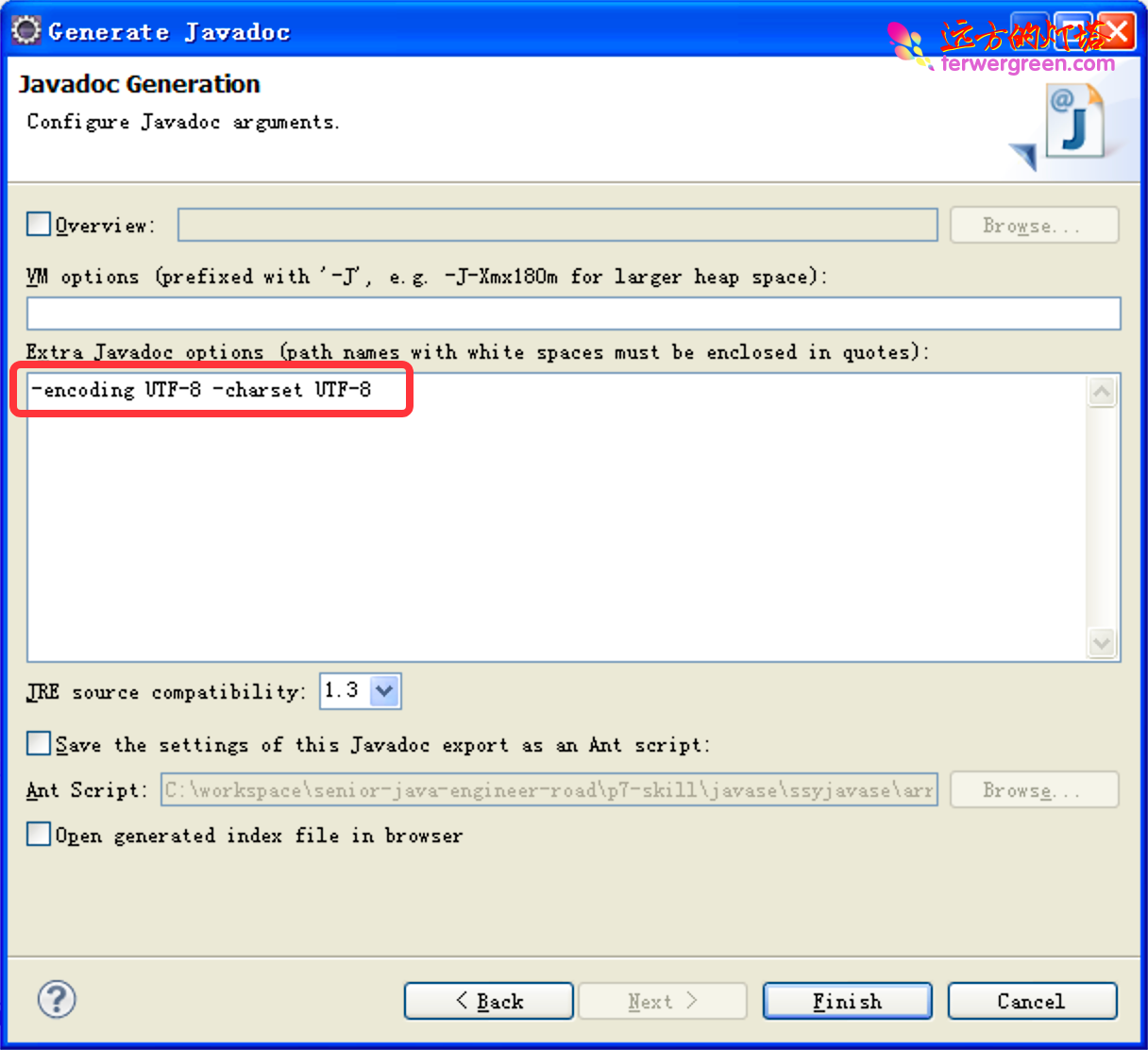
效果