在 MyBatis 中,一级缓存是默认开启的。
通过场景来理解:
场景一
1、在一个 SqlSession 中,对 User 表进行两次根据 ID 的查询,查看发出 sql 语句的情况。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
|
@Select("select * from user where id=#{id}")
User findUserById(Integer id);
@Before
public void before() throws Exception {
System.out.println("before...");
InputStream resourceAsStream = Resources.getResourceAsStream("sqlMapConfig.xml");
SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(resourceAsStream);
sqlSession = sqlSessionFactory.openSession();
userMapper = sqlSession.getMapper(IUserMapper.class);
}
@Test
public void testFindUserById() {
User user = userMapper.findUserById(1);
System.out.println(user);
User user2 = userMapper.findUserById(1);
System.out.println(user2);
}
|
sql 执行过程如下:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
| Setting autocommit to false on JDBC Connection [com.mysql.cj.jdbc.ConnectionImpl@1677d1]
==> Preparing: select * from user where id=?
==> Parameters: 1(Integer)
<== Columns: id, username, password, birthday
<== Row: 1, lucy, 123, 2019-12-12
<== Total: 1
User{id=1, username='lucy', orderList=null, roleList=null}
User{id=1, username='lucy', orderList=null, roleList=null}
Process finished with exit code 0
|

场景二
2、同样对 user 表进行两次查询,不同的是两次查询之间进行了一次 update 操作
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
| @Test
public void testFindUserById2() {
User user = userMapper.findUserById(1);
System.out.println(user);
user.setUsername("tyw");
userMapper.update(user);
User user2 = userMapper.findUserById(1);
System.out.println(user2);
}
|
可以看到,第一次查询后,进行了更新,然后进行第二次查询,这里两次查询都输出了 sql,说明缓存没有生效。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
| Setting autocommit to false on JDBC Connection [com.mysql.cj.jdbc.ConnectionImpl@48fa0f47]
==> Preparing: select * from user where id=?
==> Parameters: 1(Integer)
<== Columns: id, username, password, birthday
<== Row: 1, lucy, 123, 2019-12-12
<== Total: 1
User{id=1, username='lucy', orderList=null, roleList=null}
==> Preparing: update user set username=? where id=?
==> Parameters: tyw(String), 1(Integer)
<== Updates: 1
==> Preparing: select * from user where id=?
==> Parameters: 1(Integer)
<== Columns: id, username, password, birthday
<== Row: 1, tyw, 123, 2019-12-12
<== Total: 1
User{id=1, username='tyw', orderList=null, roleList=null}
|
总结
1、第一次查询用户 ID 为 1 的用户信息,先去缓存查找有没有 ID 为 1 的用户信息,如果没有,从数据库查询用户信息。得到用户信息,将数据保存到一级缓存中。
2、如果 SqlSession 执行了 commit 操作(执行插入、更新、删除),则会情况 SqlSession 的一级缓存。这样做的目的是保存一级缓存中额数据是最新数据,防止脏读。
3、第二次发起查询 ID 为 1 的用户信息,先去缓存中查询 ID 为 1 的用户信息,如果有,直接返回。
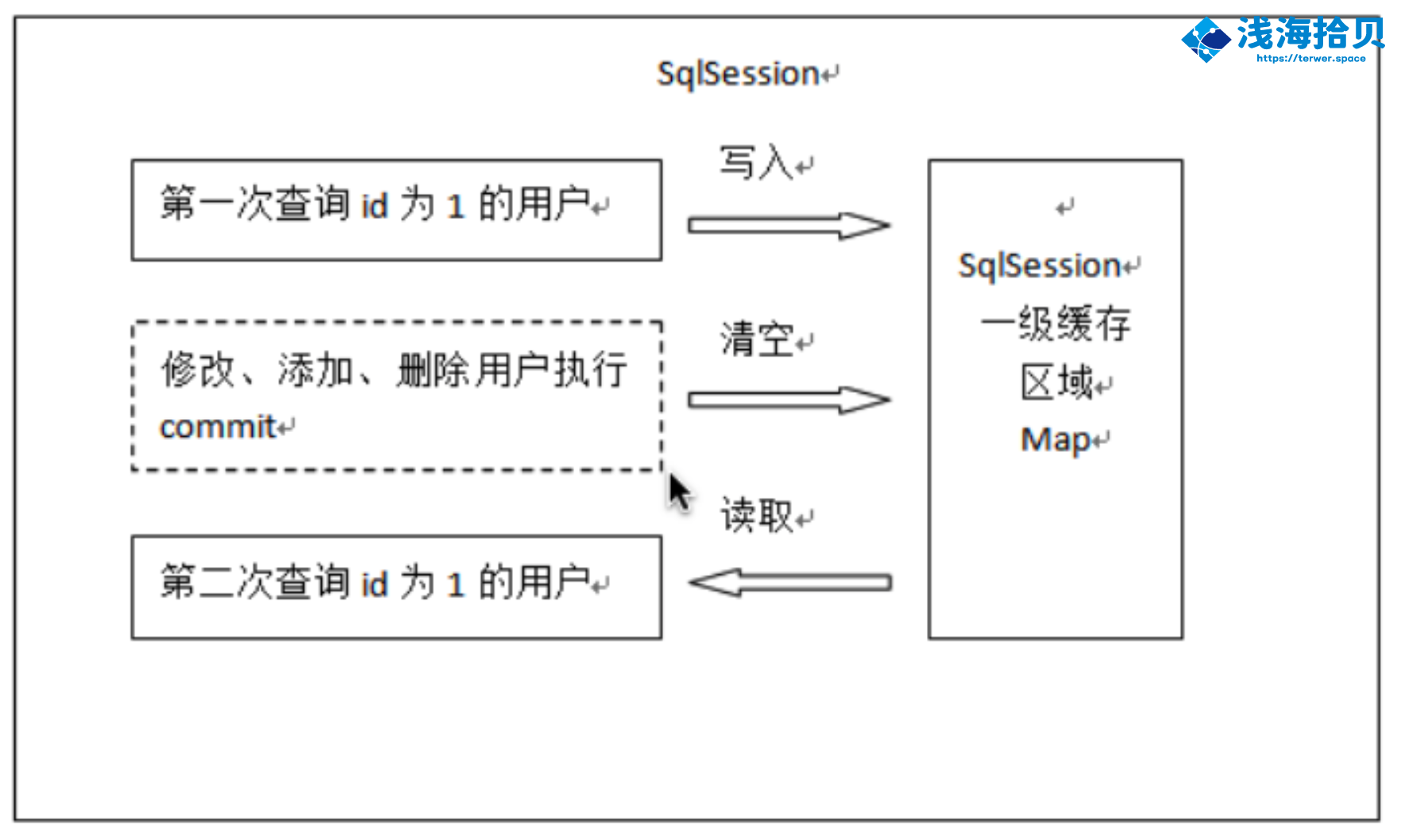
一级缓存查找过程
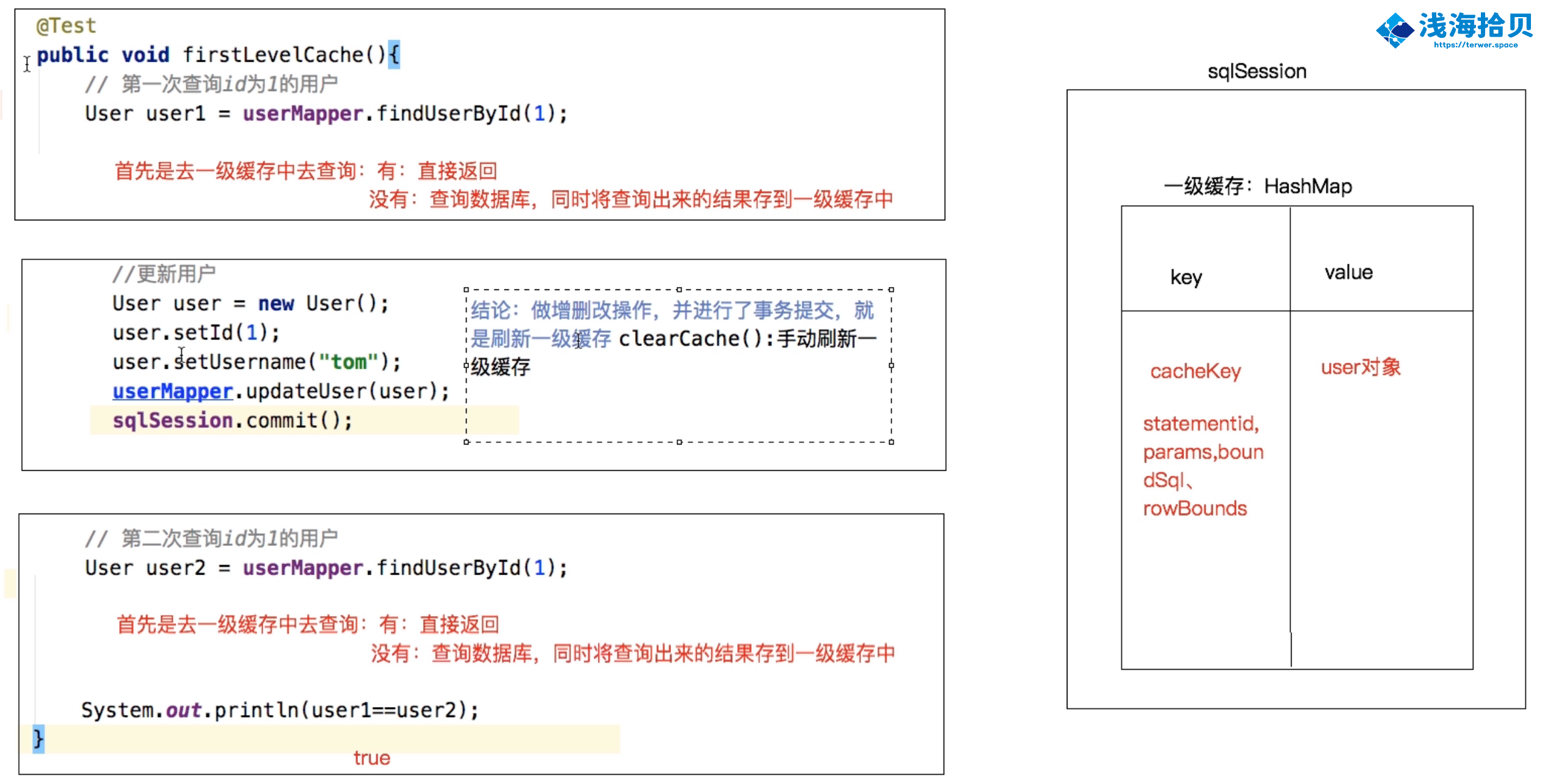
一级缓存原理探究与源码分析
问题抛出
一级缓存是什么?一级缓存什么时候被创建?一级缓存的工作流程是什么?
SqlSession 中与缓存相关的属性和方法
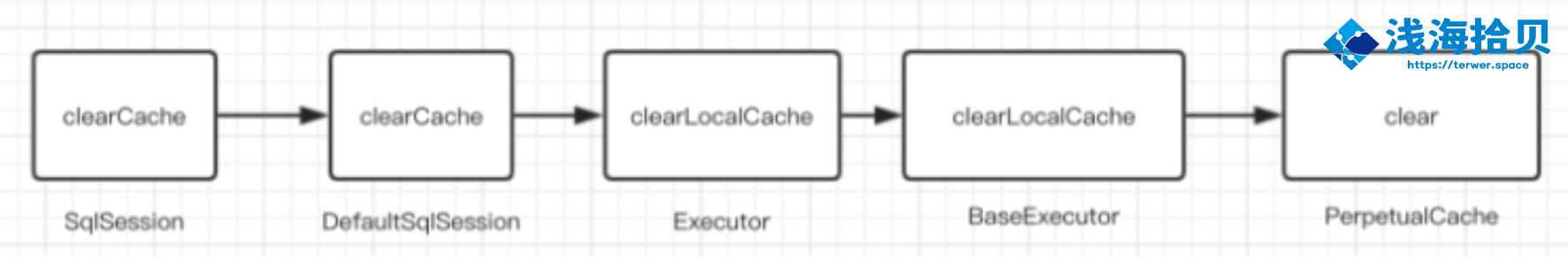
跟踪一下 clearCache 的子类和父类
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
| @startuml
!include https://unpkg.com/plantuml-style-c4@latest/core.puml
' uncomment the following line and comment the first to use locally
'!include core.puml
'!theme plain
top to bottom direction
skinparam linetype ortho
class BaseExecutor
class DefaultSqlSession
class PerpetualCache
interface SqlSession << interface >>
BaseExecutor -[#595959,dashed]-> PerpetualCache : "«create»"
BaseExecutor "1" *-[#595959,plain]-> "localCache\n1" PerpetualCache
DefaultSqlSession -[#008200,dashed]-^ SqlSession
@enduml
|
简单来看
 可以看到,cache 的最底层其实就是一个 HashMap
可以看到,cache 的最底层其实就是一个 HashMap
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
| public class PerpetualCache implements Cache {
private final String id;
private final Map<Object, Object> cache = new HashMap<>();
...
}
|
缓存其实就是本地存放的一个 Map 对象,每一个 SqlSession 都会存放一个 map 对象的引用。
cache 的创建时机
Executor 是执行器,用来执行 SQL 请求,而且清除缓存的方法也在 Executor 中执行,所以很可能缓存的创建也很 有可能在 Executor 中。
Executor 中有一个 createCacheKey 方法,这个方法很像是创建缓存的方法,跟进去看看,发现 createCacheKey 方法是由 BaseExecutor 执行的,代码如下
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
| @Override
public CacheKey createCacheKey(MappedStatement ms, Object parameterObject, RowBounds rowBounds, BoundSql boundSql) {
if (closed) {
throw new ExecutorException("Executor was closed.");
}
CacheKey cacheKey = new CacheKey();
cacheKey.update(ms.getId());
cacheKey.update(rowBounds.getOffset());
cacheKey.update(rowBounds.getLimit());
cacheKey.update(boundSql.getSql());
List<ParameterMapping> parameterMappings = boundSql.getParameterMappings();
TypeHandlerRegistry typeHandlerRegistry = ms.getConfiguration().getTypeHandlerRegistry();
for (ParameterMapping parameterMapping : parameterMappings) {
if (parameterMapping.getMode() != ParameterMode.OUT) {
Object value;
String propertyName = parameterMapping.getProperty();
if (boundSql.hasAdditionalParameter(propertyName)) {
value = boundSql.getAdditionalParameter(propertyName);
} else if (parameterObject == null) {
value = null;
} else if (typeHandlerRegistry.hasTypeHandler(parameterObject.getClass())) {
value = parameterObject;
} else {
MetaObject metaObject = configuration.newMetaObject(parameterObject);
value = metaObject.getValue(propertyName);
}
cacheKey.update(value);
}
}
if (configuration.getEnvironment() != null) {
cacheKey.update(configuration.getEnvironment().getId());
}
return cacheKey;
}
|
创建缓存 key 会经过一系列的 update 方法,update 方法由一个 CacheKey 这个对象来执行的,这个 update 方法最终由 updateList 的 list 来把五个值存进去。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
| public void update(Object object) {
int baseHashCode = object == null ? 1 : ArrayUtil.hashCode(object);
count++;
checksum += baseHashCode;
baseHashCode *= count;
hashcode = multiplier * hashcode + baseHashCode;
updateList.add(object);
}
|
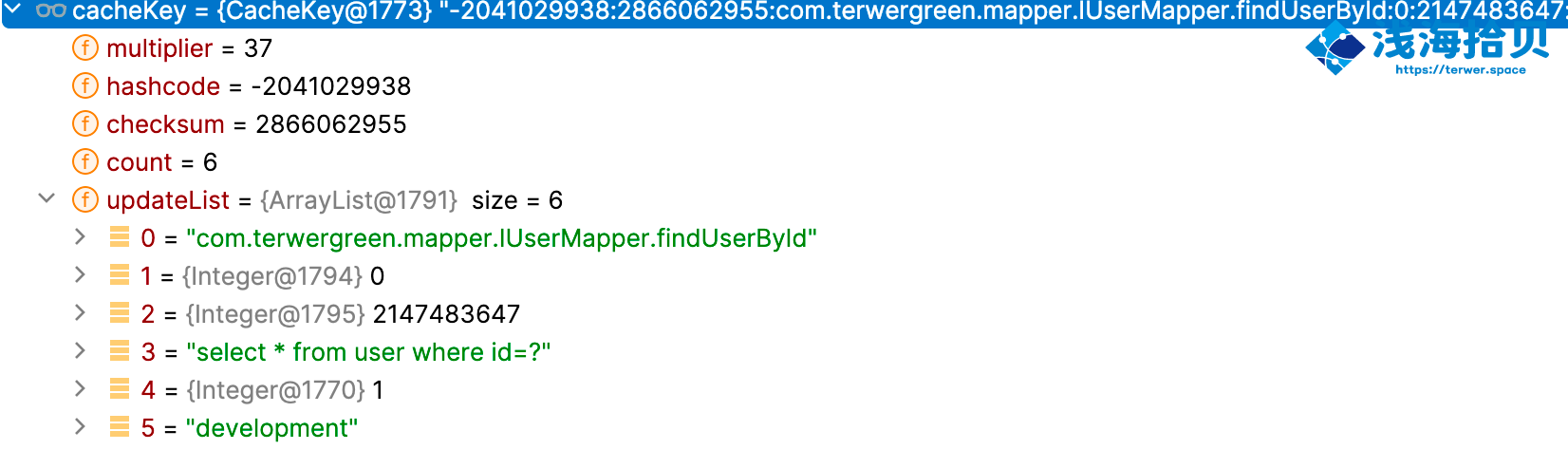
这里需要注意一下最后一个值,configuration.getEnvironmen().getId() 这是什么,这其实就是定义在 sqlMapConfig.xml 中的标签,⻅如下。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
|
<environments default="development">
<environment id="development">
<transactionManager type="JDBC"/>
<dataSource type="POOLED">
<property name="driver" value="${jdbc.driver}"/>
<property name="url" value="${jdbc.url}"/>
<property name="username" value="${jdbc.username}"/>
<property name="password" value="${jdbc.password}"/>
</dataSource>
</environment>
<environment id="production">
<transactionManager type="JDBC"/>
<dataSource type="POOLED">
<property name="driver" value="${jdbc.driver}"/>
<property name="url" value="${jdbc.url}"/>
<property name="username" value="${jdbc.username}"/>
<property name="password" value="${jdbc.password}"/>
</dataSource>
</environment>
</environments>
|
一级缓存的使用
一级缓存更多是用于查询操作,毕竟一级缓存也叫做查询缓存。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
| @Override
public <E> List<E> query(MappedStatement ms, Object parameter, RowBounds rowBounds, ResultHandler resultHandler) throws SQLException {
BoundSql boundSql = ms.getBoundSql(parameter);
CacheKey key = createCacheKey(ms, parameter, rowBounds, boundSql);
return query(ms, parameter, rowBounds, resultHandler, key, boundSql);
}
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
@Override
public <E> List<E> query(MappedStatement ms, Object parameter, RowBounds rowBounds, ResultHandler resultHandler, CacheKey key, BoundSql boundSql) throws SQLException {
ErrorContext.instance().resource(ms.getResource()).activity("executing a query").object(ms.getId());
if (closed) {
throw new ExecutorException("Executor was closed.");
}
if (queryStack == 0 && ms.isFlushCacheRequired()) {
clearLocalCache();
}
List<E> list;
try {
queryStack++;
list = resultHandler == null ? (List<E>) localCache.getObject(key) : null;
if (list != null) {
handleLocallyCachedOutputParameters(ms, key, parameter, boundSql);
} else {
list = queryFromDatabase(ms, parameter, rowBounds, resultHandler, key, boundSql);
}
} finally {
queryStack--;
}
if (queryStack == 0) {
for (BaseExecutor.DeferredLoad deferredLoad : deferredLoads) {
deferredLoad.load();
}
deferredLoads.clear();
if (configuration.getLocalCacheScope() == LocalCacheScope.STATEMENT) {
clearLocalCache();
}
}
return list;
}
|
queryFromDatabase 方法
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
| private <E> List<E> queryFromDatabase(MappedStatement ms, Object parameter, RowBounds rowBounds, ResultHandler resultHandler, CacheKey key, BoundSql boundSql) throws SQLException {
List<E> list;
localCache.putObject(key, EXECUTION_PLACEHOLDER);
try {
list = doQuery(ms, parameter, rowBounds, resultHandler, boundSql);
} finally {
localCache.removeObject(key);
}
localCache.putObject(key, list);
if (ms.getStatementType() == StatementType.CALLABLE) {
localOutputParameterCache.putObject(key, parameter);
}
return list;
}
|
如果查不到的话,就从数据库查,在 queryFromDatabase 中,会对 localcache 进行写入。 localcache 对象的 putObject 方法调用 PerpetualCache 类 的 put 方法,最终交给 Map 进行存放。
1
2
3
4
| @Override
public void putObject(Object key, Object value) {
cache.put(key, value);
}
|




 可以看到,cache 的最底层其实就是一个 HashMap
可以看到,cache 的最底层其实就是一个 HashMap

