NIO三大核心之选择器(Selector)
选择器(Selector)
基本介绍
用一个线程,处理多个客户端连接,就会用到NIO的Selector(选择器)。
Selector能够检测多个注册的服务端通道上是否有事件发生。如果有事件发生,便获取事件,然后针对每个事件进行响应的处理。
这样可以用单线程去管理多个通道,也就是管理多个连接和请求。
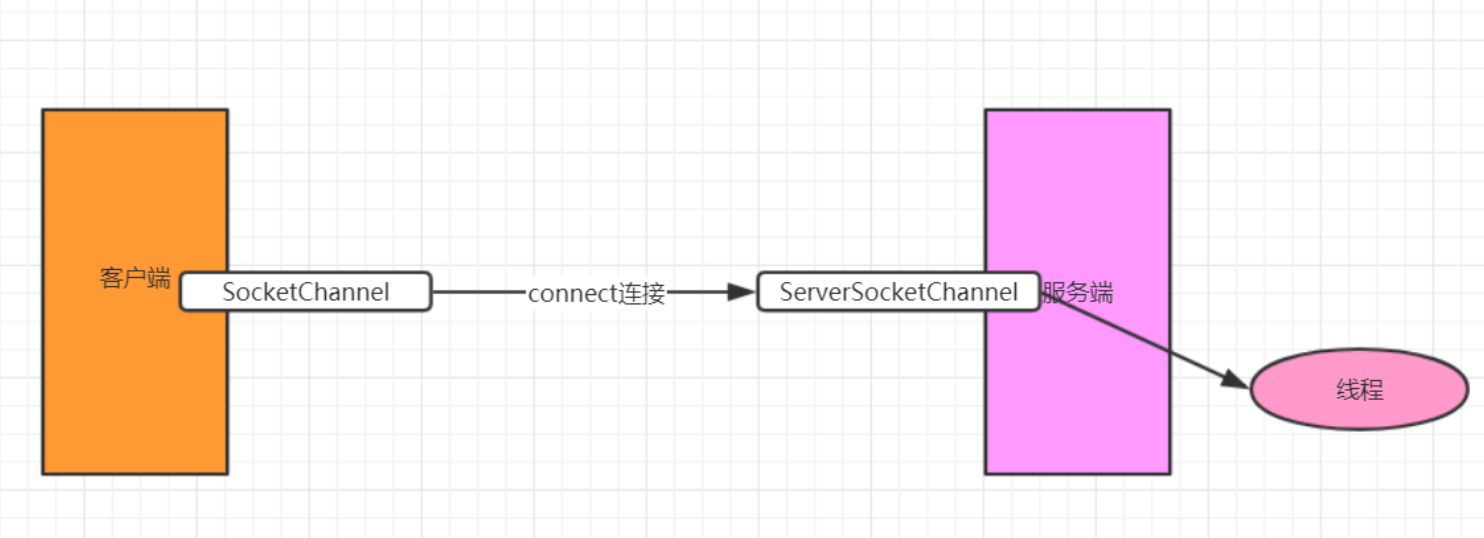
在没有选择器的情况下,每个连接对应一个请求,但是连接不能马上发送消息,所以会产生资源浪费。
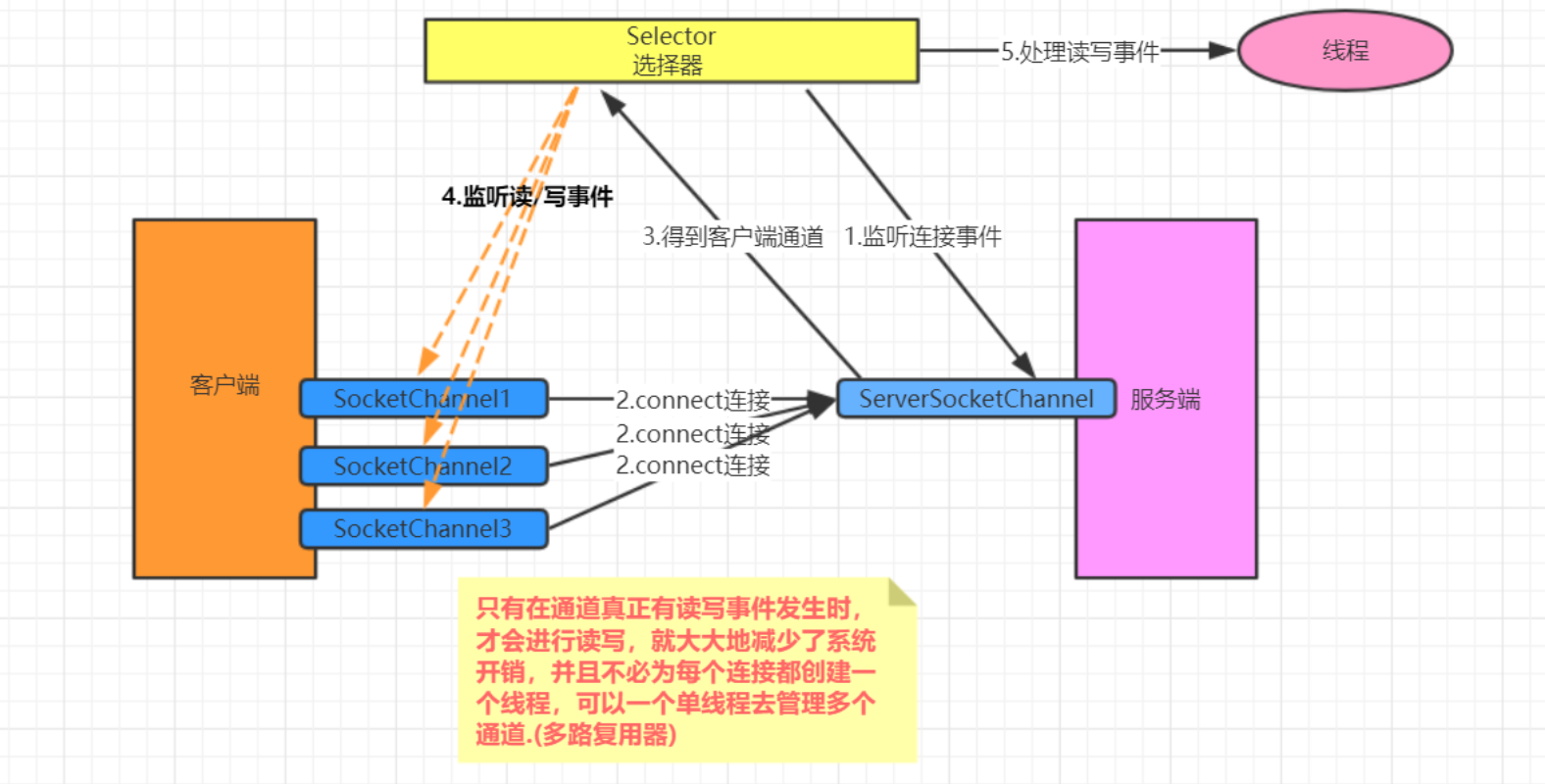
有了选择器之后,只有在通道真正有读写事件发生时,才会进行读写。这样大大减小了系统开销,不必为每个连接创建一个线程,不用去维护多个线程,避免了多线程上下文切换导致的开销。
常用API介绍
Selector是一个抽象类
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10classDiagram
direction BT
class KQueueSelectorImpl
class PollSelectorImpl
class Selector
class SelectorImpl
KQueueSelectorImpl --> SelectorImpl
PollSelectorImpl --> SelectorImpl
SelectorImpl --> Selector如果图片无法查看,请看这里
常用方法:
Selector.open();// 得到一个选择器对象
Selector.select();// 阻塞,监控所有注册的通道,当有对应的事件时,会将SelectionKey放入集合内部并返回事件数量
Selector.select(1000);// 阻塞1000毫秒,监控所有注册的通道,当有对应的事件时,会将SelectionKey放入集合内部并返回
Selector.selectedKeys;// 返回存有SelectionKey的集合
SelectionKey
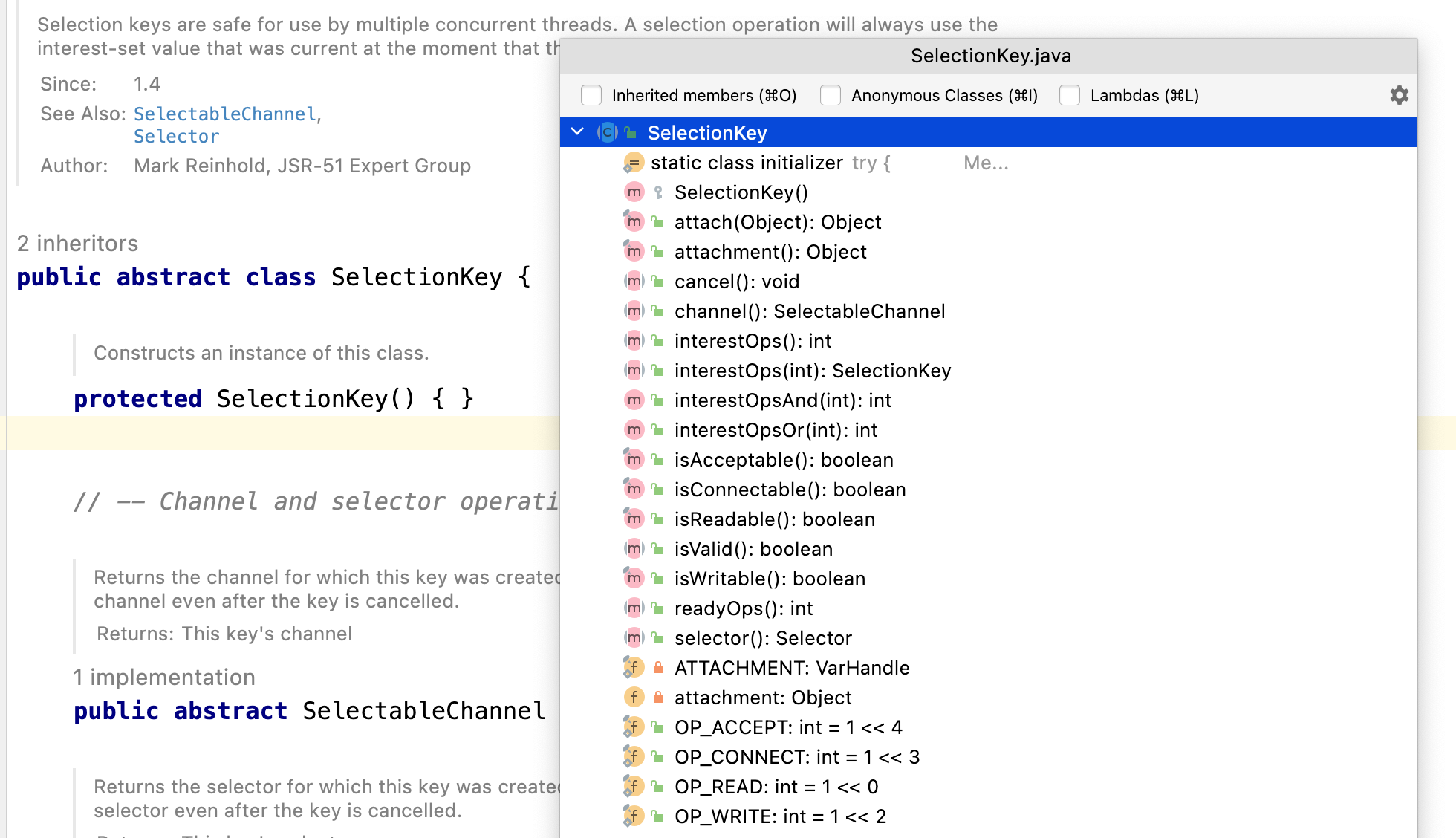
- 常用方法
- SelectionKey.isAcceptable();// 是否是连接继续事件
- SelectionKey.isConnectable();// 是否是连接就绪事件
- SelectionKey.isReadable();// 是否是读就绪事件
- SelectionKey.isWritable();// 是否是写就绪事件
- SelectionKey中定义的4种事件
- SelectionKey.OP_ACCEPT;// 接收连接继续事件,表示服务器监听到了客户端连接,服务器可以接受这个连接了
- SelectionKey.OP_CONNECT;// 连接就绪事件,表示客户端与服务器连接已经建立成功
- SelectionKey.OP_READ;// 读就绪事件,表示通道中已经有了可以读取的数据,可以执行读操作
- SelectionKey.OP_WRITE;// 写就绪事件,表示可以向通道写数据了
- 常用方法
Selector编码
服务端
实现步骤
- 打开一个服务端通道
- 绑定对应的端口号
- 通道默认是阻塞的,需要设置为非阻塞
- 创建选择器
- 将服务端通道注册到选择器上,并指定注册监听的事件为OP_ACCEPT
- 检查选择器是否有事件
- 获取事件集合
- 判断事件是否是客户端连接事件SelectionKey.isAcceptable()
- 得到客户端通道,并将通道注册到选择器上, 并指定监听事件为OP_READ
- 判断是否是客户端读就绪事件SelectionKey.isReadable() 11. 得到客户端通道,读取数据到缓冲区
- 给客户端回写数据
- 从集合中删除对应的事件, 因为防止二次处理.
代码实现
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68/**
* 基于选择器实现服务端
*
* @name: NIOSelectorServer
* @author: terwer
* @date: 2022-04-18 23:07
**/
public class NIOSelectorServer {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
// 1. 打开一个服务端通道
ServerSocketChannel serverSocketChannel = ServerSocketChannel.open();
// 2. 绑定对应的端口号
serverSocketChannel.bind(new InetSocketAddress(9999));
// 3. 通道默认是阻塞的,需要设置为非阻塞
serverSocketChannel.configureBlocking(false);
// 4. 创建选择器
Selector selector = Selector.open();
// 5. 将服务端通道注册到选择器上,并指定注册监听的事件为OP_ACCEPT
serverSocketChannel.register(selector, SelectionKey.OP_ACCEPT);
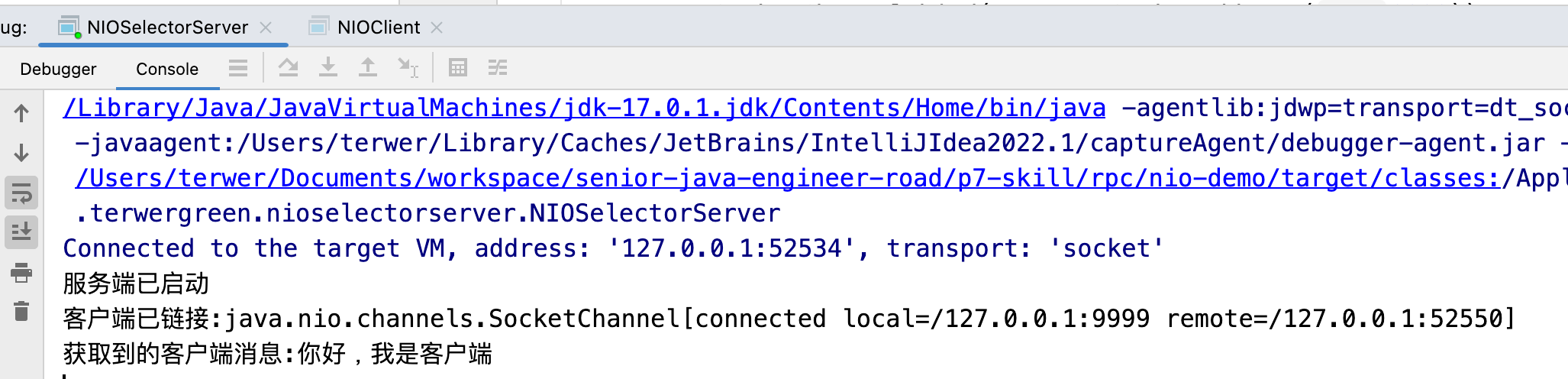
System.out.println("服务端已启动");
while (true) {
// 6. 检查选择器是否有事件
int select = selector.select(2000);
if (select == 0) {
continue;
}
// 7. 获取事件集合
Set<SelectionKey> selectionKeys = selector.selectedKeys();
Iterator<SelectionKey> iterator = selectionKeys.iterator();
while (iterator.hasNext()) {
// 8. 判断事件是否是客户端连接事件SelectionKey.isAcceptable()
SelectionKey key = iterator.next();
// 9. 得到客户端通道,并将通道注册到选择器上, 并指定监听事件为OP_READ
if (key.isAcceptable()) {
SocketChannel socketChannel = serverSocketChannel.accept();
System.out.println("客户端已链接:" + socketChannel);
// 设置为非阻塞
socketChannel.configureBlocking(false);
socketChannel.register(selector, SelectionKey.OP_READ);
}
// 10. 判断是否是客户端读就绪事件SelectionKey.isReadable()
if (key.isReadable()) {
// 11. 得到客户端通道,读取数据到缓冲区
SocketChannel channel = (SocketChannel) key.channel();
ByteBuffer byteBuffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(1024);
int read = channel.read(byteBuffer);
if (read > 0) {
System.out.println("获取到的客户端消息:" + new String(byteBuffer.array(), 0, read));
// 12. 给客户端回写数据
channel.write(ByteBuffer.wrap("给客户端的回复".getBytes(StandardCharsets.UTF_8)));
channel.close();
}
}
// 13. 从集合中删除对应的事件, 因为防止二次处理.
iterator.remove();
}
}
}
}
客户端
同NIOClient。
运行结果
NIO三大核心之选择器(Selector)
https://hexo.terwer.space/post/selector-of-nio-three-cores.html

